Banyan Security FAQ
What is the Banyan Security Platform?What does Banyan Security do?
Yet this creates tremendous challenges for securing this ever-growing and interconnected access surface to protect information, ensure compliance, catalyze innovation, and deliver an outstanding user experience.
At Banyan Security, we help IT and Security teams successfully deliver modern secure remote access to both today and the next generation of users and applications.
Our Security Service Edge (SSE) solution – the Banyan Security Platform provides secure, zero trust “work from anywhere” access to applications and resources for employees and third parties while protecting them from being phished, straying onto malicious web sites, or being exposed to ransomware. A Flexible Edge architecture enables rapid, incremental deployment on-premises or in the cloud without compromising privacy or data sovereignty. A unique device-centric approach intelligently routes traffic for optimal performance and security delivering a great end user experience. Built on a patented Zero Trust architecture, the Banyan solution transparently deploys in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, continuously enforcing trust-based access policies based on any combination of user, device, and application contexts.
How does the Banyan Security Platform work?
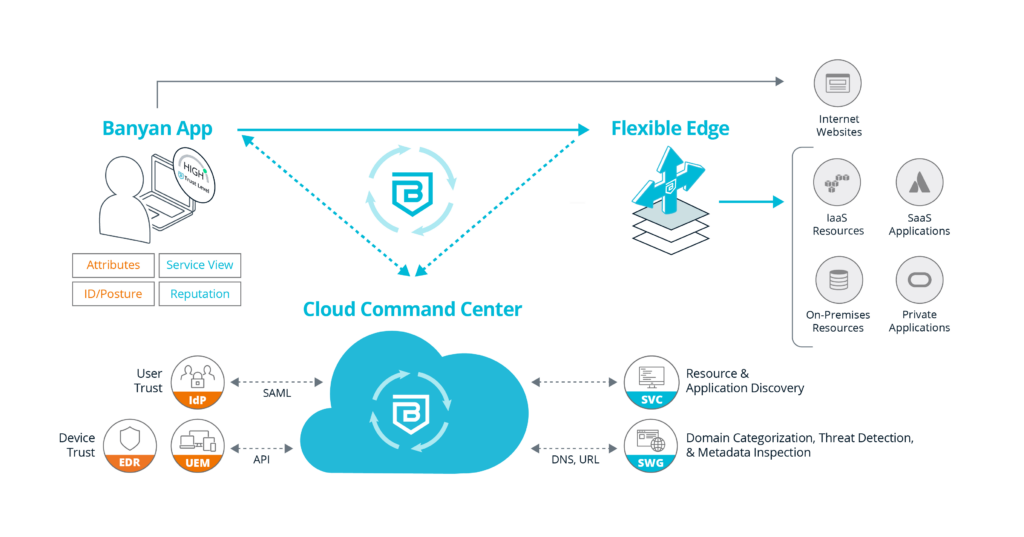
Banyan makes access to private networks easy and secure for everyone, from small teams to global enterprises. We’ll dive into how it works by looking at the main components:
- The Cloud Command Center is our cloud-based management and visibility platform which integrates with various services, such as IdP, EDR, and UEM to learn about the user and devices. It also integrates with threat feeds to provide enforcement policies on outbound traffic. The Cloud Command Center also provides discover and publish functionality, allowing enterprises to quickly locate resources and create least privilege access to them, whether they are on-premises, in SaaS, or IaaS.
- Flexible Edge enables easy deployment anywhere your resources live. The Flexible Edge provides a multi-cloud identity-aware access proxy that securely cloaks cloud applications and servers from malicious attacks or inadvertent exposure and also provides real-time enforcement of accessibility due to policy infractions. Flexible Edge can be easily deployed using tarball, Docker, and Terraform.
- The Banyan app, available on desktop and mobile, is recommended but not required. The Banyan app provides VPNaaS and ZTNA connectivity, along with making SWG and CASB decisions. The Banyan app is also used to gain visibility into the device for real-time Device Trust insights. The Banyan app communicates with the Cloud Command Center for authentication and authorization decisions, aka control plane communication. It also communicates directly with the Flexible Edge for all data plane related activities.
#image_title
Can I replace my legacy VPN with the Banyan Security Platform?
Yes! Banyan’s Security Service Edge (SSE) solution provides seamless remote access to employees and third-parties while eliminating massive security gaps, streamlining IT management, and removing choke-points for your users.
The Banyan Security Platform enforces least-privileged access to applications and services in real-time, leveraging your existing enterprise identity and security tool investments. Built on a patented zero trust architecture, the Banyan solution transparently deploys in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, continuously enforcing trust-based access policies based on any combination of user, device, and application contexts.
Can I deploy ZTNA and keep my existing VPN?
No problem! The Banyan Security Platform’s Zero Trust Network Access solution can be deployed alongside existing infrastructure – no need to rip and replace. Banyan offers an incremental “deploy-as-you-go” model for admins and users that includes co-existence with VPNs, one app or service at a time, permissive mode (learning) vs. enforcing, and more.
Is an endpoint client required for the Banyan Security Platform?
Banyan’s Security Service Edge (SSE) solution can be deployed without an endpoint client; however, you get some important benefits by using the lightweight Banyan app. Banyan delivers a robust Device Trust solution featuring passwordless access that takes advantage of a lightweight app that can be easily installed by the end user or silently deployed by the administrators. Unlike MDM and UEM products, the Banyan app does not provide any administrative control over the end user’s personal device, making it attractive for employer-owned and BYOD (employees, contractors, etc.) devices alike.
What is the Banyan app? Is it required?
The Banyan app is a cross-platform endpoint client, installed on end user desktop and mobile devices. The app is used to register and authenticate end user devices with the Banyan Cloud Command Center. Note that the Banyan app is optional on MDM-managed devices on which you can install a Device Certificate via your device manager.
The Banyan app allows users to self-register devices and enjoy one-click access to a personalized catalog of corporate resources (websites, applications, services, infrastructure, etc.)
Should users be concerned about privacy with the Banyan app?
The Banyan app was developed with privacy in mind.

What threats should I be aware of from AI tools?
How are traditional vendors handling these threats?
How does Banyan help protect against AI-based threats?
-
Discovery: Banyan can discover and categorize thousands of SaaS applications as well as web-based applications deployed on-premises. Once discovered, different actions can be taken.
-
Block applications: Many organizations want the ability to completely block entire categories of applications, as well as, have the ability to whitelist a single, corporate-approved application.
-
Granular actions: Other organizations want more granular controls when needed. The ability to block actions such as download/upload of files, or detect sensitive data exfiltration and block those interactions from completing.
Does Banyan SSE protect only against ChatGPT, or does this apply to other AI tools?
No. Banyan’s protection is based on an “AI Tool” category of SaaS applications which includes dozens of AI tools such as ChatGPT, Bard, HuggingFace, and many more. This category, like all our other application categories, are continuously updated to include new domains and applications.
Does Al-based threat protection require a different client?
No. The Banyan app has built-in functionality that is leveraged. Administrators can configure threat protection and end users will instantly get the protection.
How do I manage the Banyan Security Platform?
The Banyan Cloud Command Center is the central management console for IT Administrators and Security teams. You can interact with the Command Center via the web portal or the RESTful API, to develop and enforce policies, configure alerts for security events and visualize real-time connectivity.
The Cloud Command Center is a SaaS platform, connected with your enterprise identity provider, that lets users write granular policies based on user and device entitlements. The Command Center issues short-lived tokens and certificates, offering one-click access to applications and resources, while also ensuring every access granted is continuously authenticated and authorized.
What kind of automation capabilities are available in the Banyan Security Platform?
- Discover and Publish provides a streamlined way to secure access to hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructure. Banyan Security is providing customers with the following benefits:
-
- Improved time to value – Banyan Security provides a quick and effective way to create least-privileged access to your infrastructure and services.
- Scalable IaaS access management – Banyan Security provides a modern, consistent way to manage access to IaaS workloads across any cloud.
- RESTful APIs from Banyan automate security policies
- Terraform Support – Terraform is an “infrastructure as code” tool that lets users define corporate resources in human-readable configuration files. A Terraform Provider is a plugin that lets users manage external APIs, facilitating Terraform’s communications with various cloud providers, databases, and services. Learn more here.
How do I get started?
Banyan can help you identify a meaningful remote access project and configure your environment for a zero trust security posture. And best of all, it is designed for an incremental rollout in any environment, integrating with existing EDR, MDM/UEM, and SIEM solutions. You can even deploy it alongside your existing VPN as you evolve your network infrastructure.
Speak with our Zero Trust experts about your security initiatives.
Can I really deploy Banyan Security’s solution in less than 15 minutes?
Yes! You can get the Banyan Security Platform Team Edition installed, deployed and adding value in less than 15 minutes. Here’s a video showing Dr. Chase Cunningham deploying the Banyan solution in his environment.
Why choose the Banyan Security Platform?
- Easy to deploy and use – most folks are up and running in 15 minutes or less, delivering an end-user experience that is superior to other forms of remote access.
- Actionable insights – Banyan offers actionable insights through deep visibility into the applications, services, users, devices, and activity that are present, which permits superior control and accountability.
- High security – the Banyan Security Platform is built on a foundation of zero trust principles that dramatically improve your organization’s security posture. These features include least privilege access, continuous authorization that leverages real-time device posture and trust, user trust, and resource sensitivity as defined in granular policy controls.
What is VDI?
VDI stands for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. It is a technology that allows users to access and use a virtualized desktop environment hosted on a centralized server or data center. Instead of having a physical computer with all the applications and data stored locally, VDI provides a virtual desktop experience where the desktop and applications run on a server and are delivered to the user’s device over the network.
What does VDI stand for?
VDI stands for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure.
What does a VPN do?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure and encrypted connection between a user’s device (computer, smartphone, etc.) and a remote server or network. It allows users to access the internet or private networks securely, preserving their privacy and data integrity. VPNs are commonly used to protect sensitive information while using public Wi-Fi, bypass regional restrictions, and access resources in a private network remotely.
What is Citrix VDI?
Citrix VDI is a specific implementation of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure provided by Citrix, a technology company specializing in virtualization, networking, and cloud services. Citrix VDI allows businesses to deliver virtual desktops and applications to end-users securely and efficiently.
What does VDI mean?
VDI means Virtual Desktop Infrastructure.
What is VDI and how it works?
I’ve already answered this question above, but to summarize, VDI is a technology that hosts virtualized desktop environments on a centralized server or data center. Users access their virtual desktops and applications remotely through their devices, and the actual processing and data storage occur on the server.
What is VDI desktop?
VDI desktop refers to the virtual desktop environment delivered to the end-user through the Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. It consists of the operating system, applications, and user settings, all running on a remote server and accessed by the user’s device.
What is VDI access?
VDI access refers to the ability of users to connect to and use their virtual desktops and applications through the Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. It involves securely authenticating the user and delivering the virtual desktop environment to their device over the network.
How VDI works?
VDI works by hosting virtual desktop environments on a centralized server or data center. When a user wants to access their virtual desktop, they connect to the server through a client application installed on their device. The client application communicates with the VDI infrastructure, and the server sends the virtual desktop screen and responds to the user’s interactions, creating a seamless user experience.
What Is SOC 2 Compliance?
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) compliance is a framework developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) to assess and report on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of a service organization’s systems. It is an auditing procedure to ensure that the organization’s data management and security practices meet the required standards and protect customer data.
How to set up a VPN?
- Subscribe to a reputable VPN service.
- Download and install the VPN app on your device.
- Launch the app and log in using your credentials.
- Choose a server location (usually, the app will connect you to the fastest server by default).
- Click the “Connect” button to establish the VPN connection.
- Once connected, your internet traffic will be encrypted and routed through the VPN server.
How to get a VPN?
- Research and choose a VPN service provider that suits your needs.
- Visit the VPN provider’s website and sign up for an account.
- Select a subscription plan and make the necessary payment.
- Download and install the VPN app for your device (Windows, Mac, Android, iOS, etc.).
- Log in to the app using your credentials.
- Connect to a server location and start using the VPN.
What does VPN stand for?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network.
What is a VPN?
I’ve answered this question before, but to reiterate, a VPN is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection between a user’s device and a remote server or network. It allows users to access the internet or private networks securely, protecting their privacy and data.
What is the best VPN?
The “best” VPN depends on your specific needs and preferences. Different VPNs offer various features, server locations, speeds, and security levels. Some popular VPN services as of my last update in September 2021 include ExpressVPN, NordVPN, CyberGhost, and Surfshark. It’s essential to research and read reviews to find the one that best fits your requirements.
What is ZTNA?
ZTNA stands for Zero Trust Network Access. It is a security model and architecture that focuses on authenticating users and devices before granting access to specific resources, regardless of whether the user is inside or outside the corporate network. The Zero Trust approach aims to reduce the risk of data breaches by assuming that no device or user should be trusted by default.
What is SASE?
SASE stands for Secure Access Service Edge. It is a networking model that combines networking and security functions into a single cloud-based service. SASE integrates features like SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) and security services like firewall, VPN, and web security, delivering them as a unified, cloud-native solution.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security concept and framework that assumes no device or user should be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the corporate network. It requires verifying and validating every user and device before granting access to specific resources, thus reducing the risk of potential data breaches.
What is the Zero Trust security model?
The Zero Trust security model is a security approach that operates on the principle of not trusting anything by default. It requires continuous verification of users, devices, and applications before granting access to resources. This model emphasizes the importance of strong authentication, least privilege access, and monitoring for potential security threats.
What is Zero Trust architecture?
Zero Trust architecture is a security framework that implements the Zero Trust security model. It involves designing and deploying security solutions that authenticate and authorize users and devices before granting access to applications and data. Zero Trust architecture typically employs multifactor authentication, encryption, micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring to enhance security.
What does Zero Trust mean?
Zero Trust means that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location or previous authentication. Every access request must be verified and authorized, and continuous monitoring ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources.
What is a Zero Trust network?
A Zero Trust network is a network infrastructure that operates based on the Zero Trust security model. It assumes that all devices, users, and applications are potentially untrusted and requires strong authentication and authorization before granting access to network resources.
What are the benefits of using ZTNA?
- Improved security: ZTNA ensures that only authorized users and devices can access specific resources, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Flexibility: ZTNA allows secure access from any location and any device, enabling remote and mobile work.
- Reduced attack surface: By applying least privilege access and micro-segmentation, ZTNA limits exposure to potential security threats.
- Simplified management: ZTNA can provide centralized control over user access, making it easier to manage and monitor access permissions.
- Compliance adherence: ZTNA helps organizations meet various regulatory and compliance requirements by implementing strong security measures.
How is ZTNA different from traditional network security models?
Traditional network security models often rely on perimeter-based security, assuming that devices and users inside the corporate network are trusted. However, ZTNA operates on the Zero Trust security model, assuming that no device or user is trusted by default, regardless of their location. ZTNA focuses on authenticating and verifying users and devices before granting access to specific resources, providing a more granular and secure approach to access control.
What does ZTNA provide compared with traditional VPNs?
Compared to traditional VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), ZTNA provides more granular and context-aware access control. While VPNs typically provide access to the entire corporate network once connected, ZTNA allows organizations to control access to specific applications and resources based on the user’s identity, device posture, and other contextual factors. This approach enhances security and reduces the attack surface.
How does ZTNA work?
ZTNA works by verifying and authenticating users and devices before granting access to specific applications and resources. It operates based on the principles of Zero Trust, where no device or user is trusted by default. ZTNA solutions often utilize multifactor authentication, device posture assessment, and continuous monitoring to ensure secure access to resources.
How does ZTNA help prevent data breaches and cyber attacks?
ZTNA helps prevent data breaches and cyber attacks by strictly controlling access to resources based on strong authentication and contextual factors. By verifying user identities and assessing device security posture, ZTNA reduces the risk of unauthorized access and ensures that only legitimate users with authorized devices can access sensitive data and applications.
What type of devices can be used with ZTNA?
ZTNA is designed to work with various devices, including desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. As long as the device can connect to the internet and run the necessary client application or web browser, it can be used to access resources through a ZTNA solution.
Does my organization need special hardware or software to use ZTNA?
No, organizations do not typically need special hardware for ZTNA implementation. ZTNA solutions are often cloud-based and delivered as software-as-a-service (SaaS). Users can access resources through ZTNA using standard devices and client applications.
How secure is a Zero Trust Network Access solution?
ZTNA solutions are designed to provide a high level of security. By adopting the Zero Trust security model, they reduce the attack surface and enhance access control. However, the security level also depends on the specific ZTNA solution, its implementation, and the overall security posture of the organization.
Can I use multiple authentication methods at once when using my Zero Trust Network Access solution?
Yes, many ZTNA solutions support multiple authentication methods simultaneously. These can include passwords, biometrics, smart cards, hardware tokens, or mobile device-based authentication methods like fingerprint recognition or one-time passcodes.
Is ZTNA compatible with legacy systems and applications?
ZTNA can be compatible with legacy systems and applications to a certain extent. Some ZTNA solutions may require additional integration efforts to work seamlessly with older technologies. However, modern ZTNA solutions often provide ways to securely connect and authenticate users to legacy applications and systems.
What are some best practices for implementing ZTNA?
- Conducting a comprehensive security assessment of existing infrastructure.
- Implementing strong authentication methods, such as multifactor authentication (MFA).
- Applying the principle of least privilege to grant access only to necessary resources.
- Monitoring user and device behaviors for suspicious activities.
- Integrating ZTNA with other security solutions like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Regularly updating and patching all devices and software components.
What are some common use cases for ZTNA?
- Secure remote access for remote and mobile workers.
- Partner and third-party access to specific resources.
- Enabling BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies securely.
- Providing secure access to cloud applications and resources.
What types of organizations should consider using ZTNA?
Any organization concerned about enhancing their security posture and reducing the risk of data breaches should consider implementing ZTNA. It is particularly beneficial for organizations with remote workers, distributed teams, or reliance on cloud-based services.
What are some examples of ZTNA solutions on the market today?
- Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
- Palo Alto Networks Prisma Access
- Akamai Enterprise Application Access (EAA)
- Cisco Secure Access by Duo
Please note that the landscape of security solutions is continuously evolving, so it’s essential to research the most up-to-date options available at the time of your inquiry.
What is SD-WAN acceleration?
SD-WAN acceleration is a feature of SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) solutions that enhances the performance and efficiency of data transmission over wide area networks. It optimizes network traffic by using various techniques, such as data compression, data deduplication, and caching, to reduce latency and improve the user experience.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN stands for Software-Defined Wide Area Network. It is a technology that enables organizations to manage and optimize their wide area network (WAN) connections more efficiently. SD-WAN uses software-based controllers to dynamically route traffic over multiple connections, such as MPLS, broadband, and cellular, based on factors like cost, performance, and availability.
What is HAaaS?
HAaaS stands for High Availability as a Service. It is a cloud-based service that provides continuous, reliable access to critical applications and data by implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms. HAaaS solutions are designed to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
What is cloud-based SD-WAN?
Cloud-based SD-WAN refers to SD-WAN solutions that are hosted in the cloud, allowing organizations to manage and configure their SD-WAN infrastructure through cloud-based controllers. This approach simplifies network management, provides better scalability, and enables easy integration with cloud-based applications and services.
How does SD-WAN work for remote access?
SD-WAN can facilitate remote access by securely connecting remote workers to the corporate network. It can use various connection types, such as MPLS, broadband, or VPN, to ensure remote users can access the necessary applications and resources securely and efficiently.
How does SD-WAN work?
SD-WAN works by abstracting the control plane from the underlying hardware and using software-based controllers to manage network traffic. The SD-WAN solution analyzes real-time data to determine the best path for each packet of information, based on factors like application type, network conditions, and security requirements. This allows organizations to optimize their network performance and reduce costs.
What is a healthcare secure access system, and why is it important in the healthcare industry?
A healthcare secure access system is a technology solution designed to control and protect access to sensitive patient data, healthcare applications, and systems within healthcare organizations. It is important in the healthcare industry to ensure patient data privacy, compliance with regulations (e.g., HIPAA), prevent data breaches, and maintain the confidentiality and integrity of medical records.
How does a healthcare secure access system protect patient data and sensitive medical information?
A healthcare secure access system protects patient data by employing encryption for data in transit and at rest, strict access controls, robust authentication methods, and audit trails. These measures ensure that only authorized personnel can access and interact with patient records, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
What are the key components of a healthcare secure access system?
Key components include user authentication mechanisms (e.g., passwords, biometrics, tokens), access control policies, auditing and monitoring tools, encryption for data protection, and secure APIs for integration with other healthcare systems.
Can you explain the role of authentication in a healthcare secure access system?
Authentication verifies the identity of users attempting to access the system. It ensures that individuals are who they claim to be. In healthcare secure access systems, authentication methods like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA) are used to grant access based on valid credentials.
How does authorization work in a healthcare secure access system, and why is it crucial?
Authorization determines what resources and data a user can access after they have been authenticated. It is crucial because it limits user privileges to only what is necessary for their roles, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information.
What are some common security threats that a healthcare secure access system helps mitigate?
Common threats include unauthorized access, data breaches, insider threats, and cyberattacks. A healthcare secure access system helps mitigate these threats through strong authentication, access controls, encryption, and monitoring.
Is it necessary for healthcare organizations to comply with specific regulations when implementing a secure access system?
Yes, healthcare organizations must comply with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and other local or national data privacy laws. These regulations require strict security measures to protect patient data.
How does a healthcare secure access system facilitate remote access for healthcare professionals and staff?
It enables secure remote access through VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), secure login portals, and MFA, allowing healthcare professionals to access patient records and healthcare systems securely from remote locations.
What measures are in place to ensure the confidentiality and privacy of patient records within the system?
Measures include encryption of data, role-based access control, strict access policies, and audit trails that monitor and log user activities to prevent unauthorized access and maintain patient privacy.
Can you provide examples of multi-factor authentication methods used in healthcare secure access systems?
Examples of MFA methods include a combination of something the user knows (password), something they have (smartphone app, token), and something they are (biometrics like fingerprint or facial recognition).
How does a healthcare secure access system address the challenges of managing user credentials and access rights?
It typically includes features for password management, user provisioning, and role-based access control (RBAC) to streamline user management and ensure that users have appropriate access permissions.
Are there any best practices for training healthcare staff on using a secure access system effectively and securely?
Best practices include regular training sessions, strong password policies, teaching users to recognize phishing attempts, and emphasizing the importance of data security and patient privacy.
What happens in case of a security breach or unauthorized access within a healthcare secure access system?
In the event of a breach or unauthorized access, the system triggers alerts and notifications to appropriate personnel for immediate response. Detailed audit logs help identify the source of the breach for investigation.
Can you explain the role of encryption in securing data transmission within the system?
Encryption transforms data into unreadable text during transmission. Only authorized recipients with the decryption key can access the information, ensuring that even if intercepted, the data remains confidential.
How can healthcare organizations ensure scalability and flexibility when implementing a secure access system?
Scalability and flexibility can be achieved through cloud-based solutions, which can scale as needed and adapt to evolving healthcare requirements. Additionally, modular design allows for flexibility in adding or modifying features.
What options are available for secure mobile access to healthcare systems for doctors and nurses on the go?
Secure mobile access can be provided through dedicated mobile apps with strong authentication, VPNs, and secure browser access, ensuring that healthcare professionals can access systems securely from their mobile devices.
How does a healthcare secure access system integrate with other healthcare IT solutions, such as electronic health records (EHR) systems?
Integration is achieved through secure APIs and interoperability standards, allowing seamless data sharing between the secure access system and EHRs, ensuring continuity of patient care.
What are the potential cost savings and efficiency improvements associated with a well-implemented healthcare secure access system?
Cost savings come from reduced data breach expenses and improved efficiency in access management. It also enhances healthcare staff productivity by ensuring quick and secure access to patient data.
Are there any specific requirements or considerations for cloud-based healthcare secure access systems?
Yes, considerations include data privacy and compliance with regulations, data encryption, redundancy for reliability, and the choice of a reputable cloud service provider with healthcare expertise.
How can healthcare organizations ensure their secure access system stays up-to-date with evolving security threats?
Regular system updates, security patches, employee training, and staying informed about the latest security trends are essential for maintaining a robust healthcare secure access system.
Get started on your Zero Trust Journey.
